Farming & Agriculture
4.O INDUSTRIAL Ai
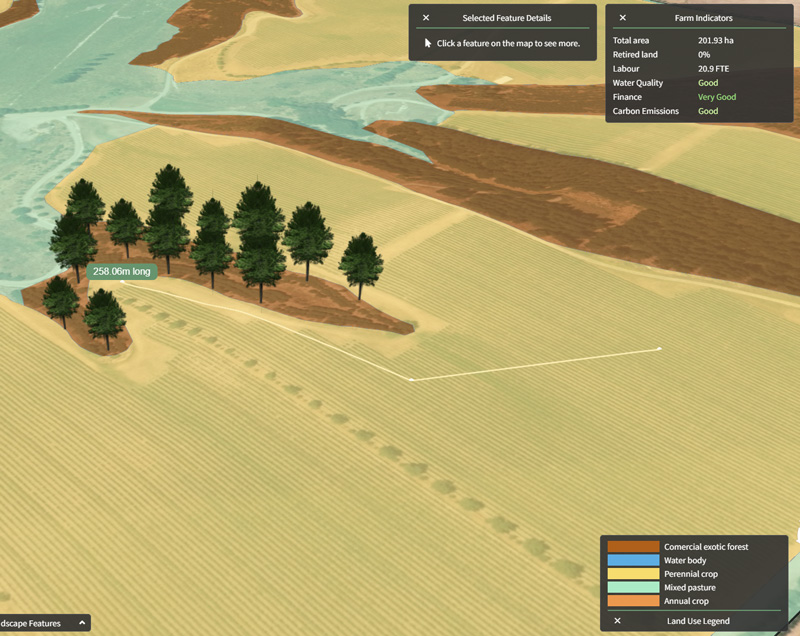
Digital Farming and Agriculture
This refers to the integration of advanced technologies, data analytics, and automation into traditional farming practices. This innovative approach to agriculture helps improve productivity, sustainability, and profitability by providing real-time insights, precision farming techniques, and better decision-making. Digital farming is often referred to as smart farming or precision agriculture and is seen as a key component in addressing global food security and environmental challenges.
4.O INDUSTRIAL Ai
Key Technologies in Digital Farming
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT-enabled devices like soil moisture sensors, climate stations, and GPS-equipped machinery gather real-time data on soil conditions, weather, and crop health. This data is used to make informed decisions.
- Big Data and Data Analytics: Data from multiple sources, such as satellite imagery, sensors, and historical crop data, is analyzed to provide insights into crop performance, predict yield, and optimize resource use.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI-powered systems help in predictive analytics, identifying patterns in data to forecast issues like pest outbreaks, optimal harvest times, or weather conditions.
- Drones and UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles): Drones equipped with multispectral cameras monitor large fields, providing farmers with high-resolution imagery and real-time information on plant health, crop growth, and pest infestations.
- Robotics and Automation: Automated systems, including robotic weeders, harvesters, and planters, reduce labor costs and increase precision in farming tasks. Autonomous tractors and machinery are becoming more common in large-scale farming.
- GPS and Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GPS-guided equipment ensures precise planting, irrigation, and fertilization, which reduces waste and improves crop yield.
REQUEST A DEMO
Let’s Talk
Have some questions that weren’t answered on the website, let us know.

